Largest Iceberg Approaches Trillion-Ton Milestone
The huge A23a Iceberg, perceived as the biggest universally, is currently measured with exact figures, uncovering its typical thickness of more than 280 meters and a complete mass moving toward a trillion tons.
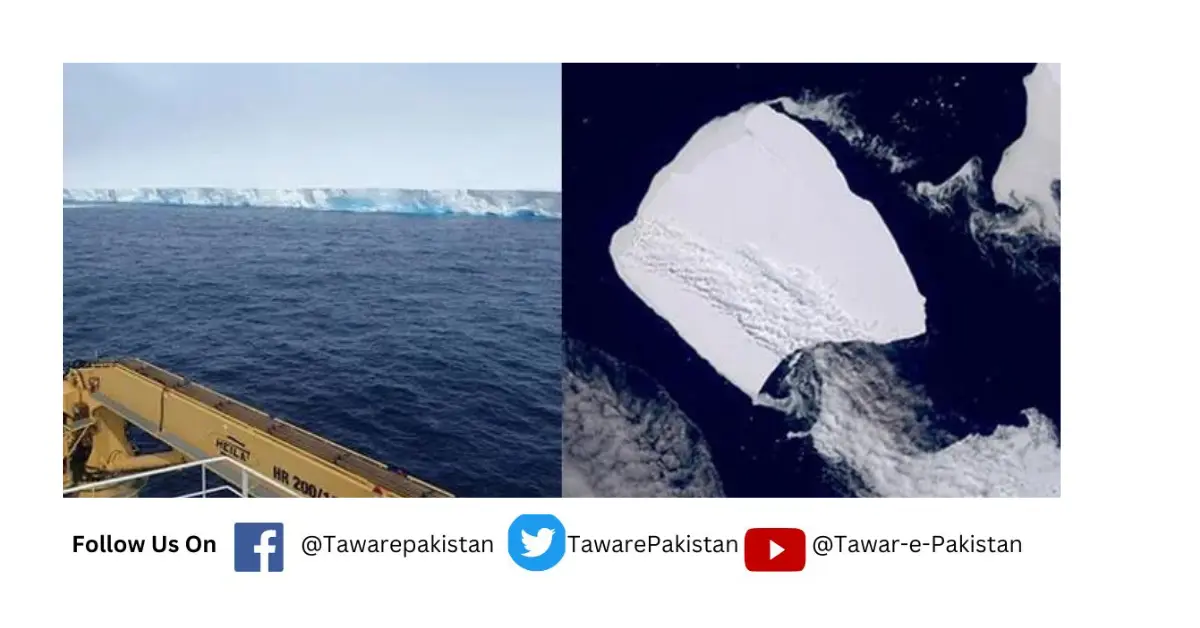
As per BBC, Calved from the Antarctic coast in 1986, A23a’s basic point in its process is unavoidable, impacting its direction through the Southern Sea before very long.
Satellite information from the European Space Office’s CryoSat-2 mission gave experiences into A23a’s perplexing construction, showing a non-uniform block for certain segments thicker than others.
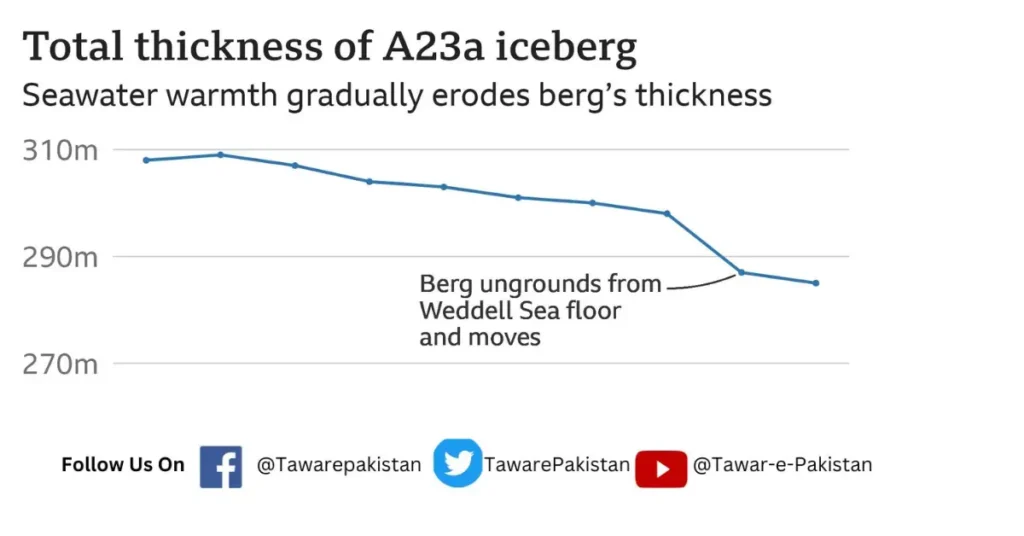
At the point when the berg began moving, after 2020, it turned out to be progressively challenging to get expansive thickness estimations. In any case, expecting an area of 3,900 sq km and a typical all out thickness of 285m, then A23a has a volume of 1,113 cubic km and a mass of 950 billion tons.
Particularly fragile is a portion with a profound fall, arriving at a draft of almost 350 meters in 2018, securing the ice sheet for over thirty years.
Satellite pictures uncover precipices straight over this fall, proposing harm caused when A23a hit the seabed during its underlying establishing.
Over the past ten years, scientists noticed a progressive reduction in thickness, averaging 2.5 meters each year, an outcome of openness to hotter waters in the Weddell Ocean.
Currently approaching at the tip of the Antarctic Promontory, A23a faces a primary phase as it experiences different tidal currents that converge around the mainland.
The iceberg’s communication with these currents, combined with winning westerly breezes, will decide its future direction. Researchers expect A23a to follow ‘icy mass back street’ guiding it towards the English overseas territory of South Georgia.
This course raises worries about its natural effect, as goliath ice shelves assume an essential part in sea elements.
Bergs of this extent actuate profound blending of seawater, cultivating supplement transport to the surface and adding to phytoplankton blossoms.
Furthermore, they discharge huge measures of residue, enhancing the encompassing sea environment. The uncovered estimations and natural ramifications highlight A23a’s significant effect on the sensitive equilibrium of the Southern Sea environment, prompting continued scrutiny and research by researchers.
Beyond News, Beyond Borders: Tawar-e-Pakistan’s Global Insight.


Comments are closed, but trackbacks and pingbacks are open.